
You must provide free annual hearing exams, hearing protection, training and evaluations. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers with noise exposure at or above 85 decibels to implement a special hearing conservation program to protect workers. Noise ViolationsĮxceeding the legal limit of noise can result in a noise violation for your business. Workplaces with noises loud enough to impair someone’s hearing will contribute to accidents when workers can’t hear the alarm. Many workplaces are equipped with warning signals to let everyone know that a door is open, a machine is on, equipment is malfunctioning and a number of other events. Other than accidents that may be caused by the issues stated above, high levels of sound may cover up important alarms or notifications. High noise levels in the workplace can lead to more accidents.
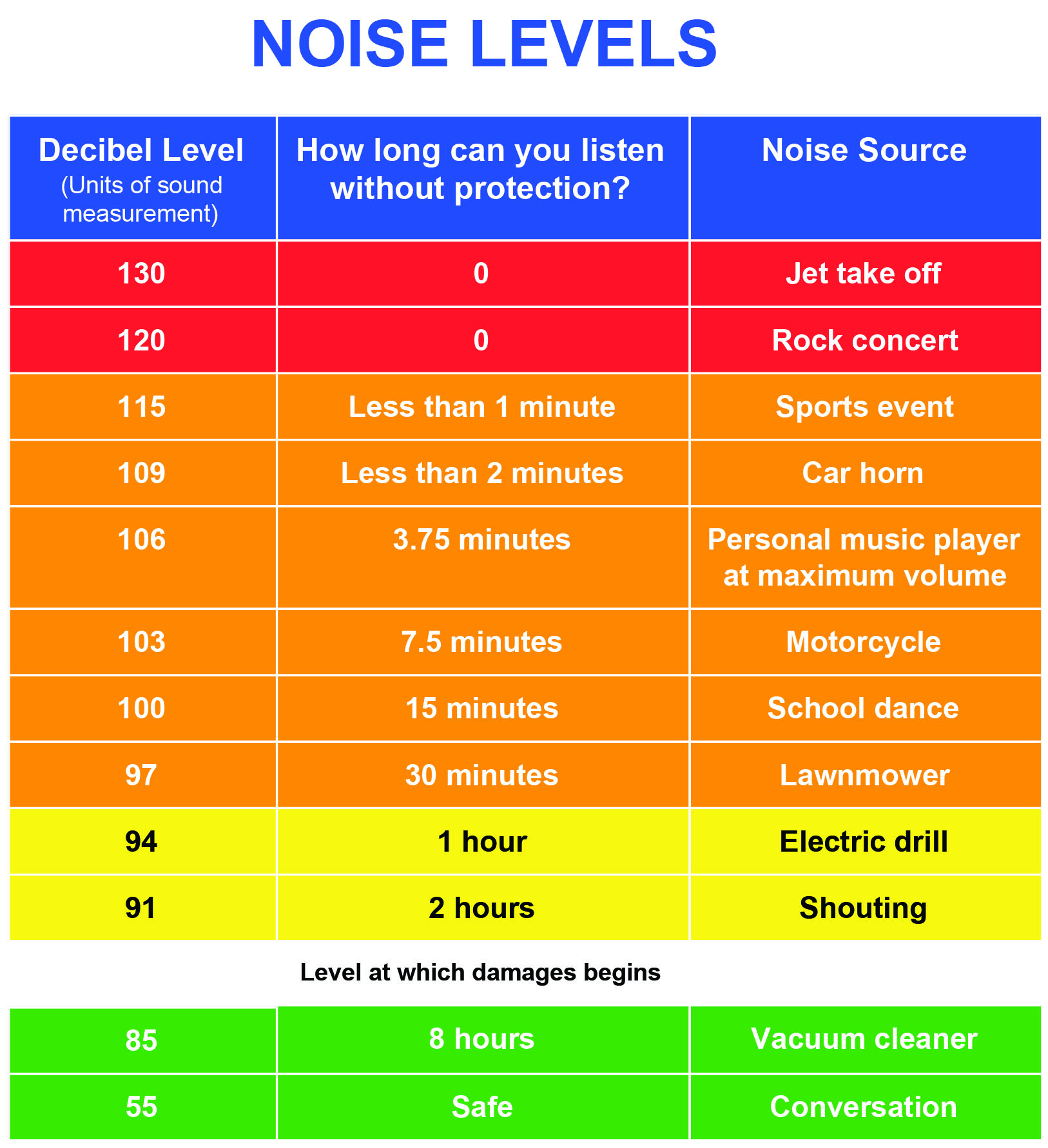
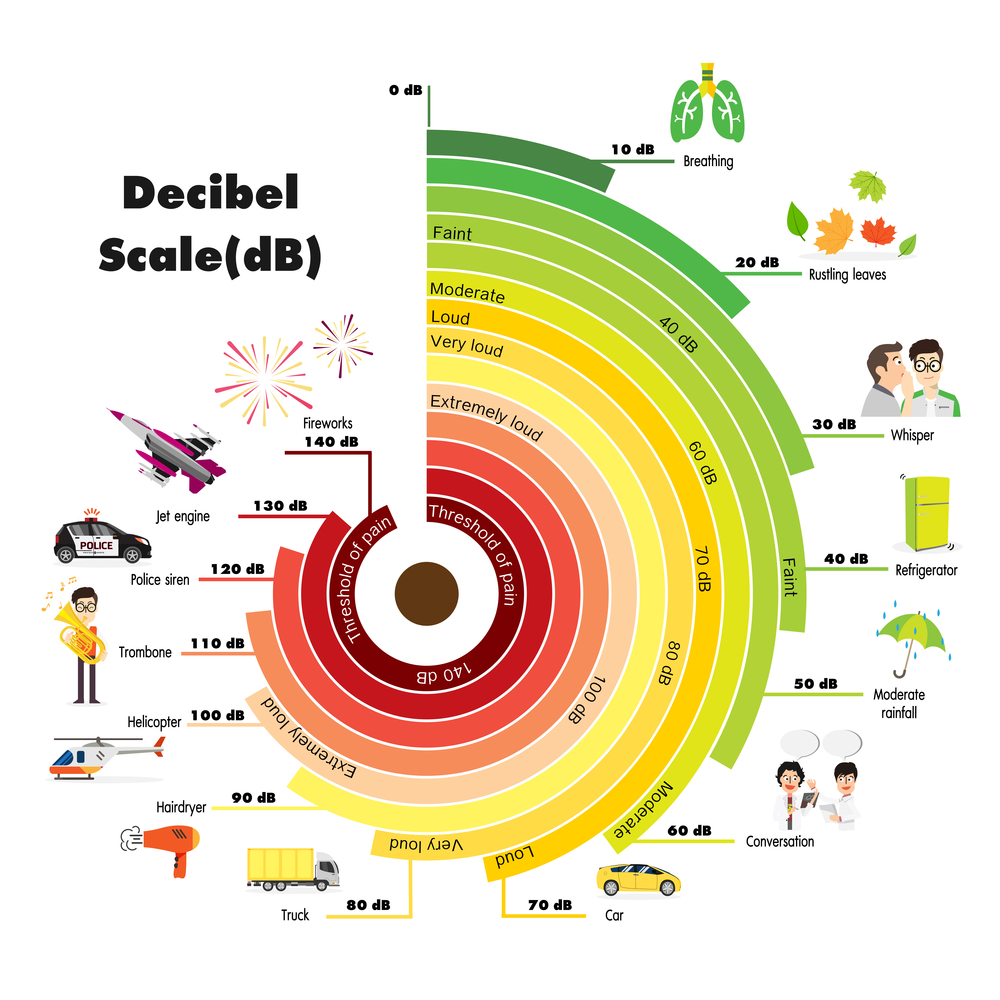
Additionally, researchers have found that certain decibel increases in noise levels are linked to a 34% increase in heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related issues. These issues continue even after leaving the noise. The stress of being in loud environments may affect more than just your ears.Ĭonsistent exposure to unsuitable levels of noise has been linked to high blood pressure, high cholesterol and increased heart rate. Diplacusis is a form of hearing loss that results in “double hearing,” where you perceive one sound as two. Sounds within safe limits can still cause pain. Hyperacusis is a disorder where you become overly sensitive to a range of sounds because they sound louder than normal. Occupational noise exposure can lead to hyperacusis and diplacusis. This is because the vibration of the sound is so strong that, over time, it damages the inner ear. The ringing in the ear may never go away, or there could be partial or complete hearing loss. Repeated exposure to loud noises can make these temporary problems turn into permanent ones. These temporary problems can last for minutes or hours after getting out of range of the noise. Your hearing may become slightly impaired and your ears may feel like they’re stuffed up. Short-term exposure to noise above a certain decibel level can result in a ringing in the ears, referred to as tinnitus. Most notably, loud noises can lead to temporary and permanent hearing loss. Your business may also suffer from noise violations and unsatisfied employees. Workers can experience numerous effects of noise exposure, including temporary and permanent hearing loss, increased physical and psychological stress, workplace accidents and more. This is why loud noises in the workplace are particularly damaging, and why legal limits for noise exist.Įmployees have to show up to work, and they often can’t go anywhere else during the workday to escape the noise. High sound levels can result in permanent health effects, especially if they occur over long periods of time or on a consistent basis. When the vibrations of the air molecules are too intense, the microscopic hairs in your inner ear can be damaged. The more intense the noise, the more likely it is for your hearing to be impaired. The higher the number of decibels, the more intense the noise. Sound is also measured in decibels, which refers to sound pressure. The longer the wave, the lower the pitch. The shorter the wave, the higher the pitch. It’s typically measured in feet or meters and has a direct relationship with frequency. The wavelength is the distance a sound wave travels during one vibration. We often refer to the frequency of a sound as its pitch, or how high or low something sounds. The frequency, measured in Hertz, is the number of vibrations that occur in one second.

The vibrations can be measured to find the frequency of the sound. Sound can be measured in a number of ways, including frequency, wavelength and sound pressure. The human ear perceives sound when air molecules vibrate and enter the ear canal, moving the microscopic hairs within the inner ear.
#Decibel levels chart how to#
Take a look at why it’s critical to protect your workers from periods of noise exposure of different levels and how to do so. When noises are too loud, employees can endure damaged hearing, increased levels of stress and more. As a result, hearing loss is the most common work-related injury in the United States, classified under exposure to harmful substances or environments. There’s no denying that noise is a common problem in many industries, with workplaces often averaging over the safe limit of sound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
